Dr. Ir. Arif Kusumawanto, M.T., IPU., a lecturer from the Department of Architecture and Planning, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), recently published a scientific paper titled “Simulation Model of Green Open Space on Microclimate Performance in Tropical Coastal Area”. This Scopus-indexed research aims to simulate scenarios of green open space to mitigate heating and improve microclimate performance. The study aligns with SDGs number 11, which focuses on sustainable cities and communities.
The research involves collaboration with academics from various institutions, including:
- Hasti Widyasamratri, S.Si., M.Eng., Ph.D. (Universitas Islam Sultan Agung)
- Dr. Hj. Mila Karmilah, ST., MT. (Universitas Islam Sultan Agung)
- Afrizal Abdi Musyafiq, S.Si., M.Eng. (Politeknik Negeri Cilacap)
- Prof. TPr. Gs. Dr. Norzailawati Mohd Noor (International Islamic University Malaysia).
Research Findings
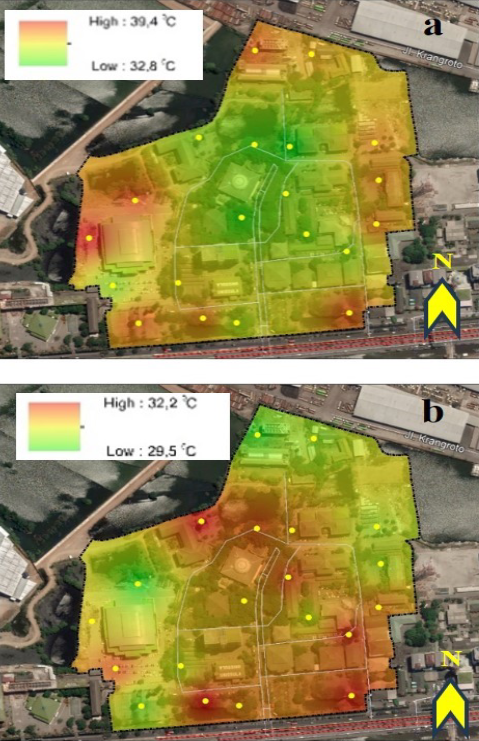
Using the ENVI-met numerical model and spatial analysis with ArcGIS, the study simulated three scenarios to mitigate heat. The results showed that a balanced composition between buildings and vegetation could reduce air temperature by 2.45°C to 3.31°C compared to simulations without greenery. Another scenario featuring “hybrid greenery” achieved a temperature decrease of up to 3.50°C compared to the current condition.
Research Conclusion
In this study, air temperature was selected as the microclimatic parameter, measured at four points, interpolated to observe spatial variation, and then simulated using ENVI-met scenario outputs. Three different scenarios were designed to address heat mitigation in the focus area. On sunny days, trees ranging from 5 to 15 meters in height reduced air temperature by distributing wind and providing shade.
The best performance was observed in Scenario 2, which featured a balanced composition of buildings and vegetation. Meanwhile, Scenario 3, which utilized hybrid greenery, showed the least effective results. Therefore, Scenario 2 demonstrated better performance in mitigating heat, as factors like high building density, trees, and surrounding built surfaces significantly influenced outdoor air temperature.
This research provides vital insights for environmentally friendly urban planning, prioritizing an optimal composition of green landscapes. Its findings serve as a valuable reference for shaping greener and more livable cities.