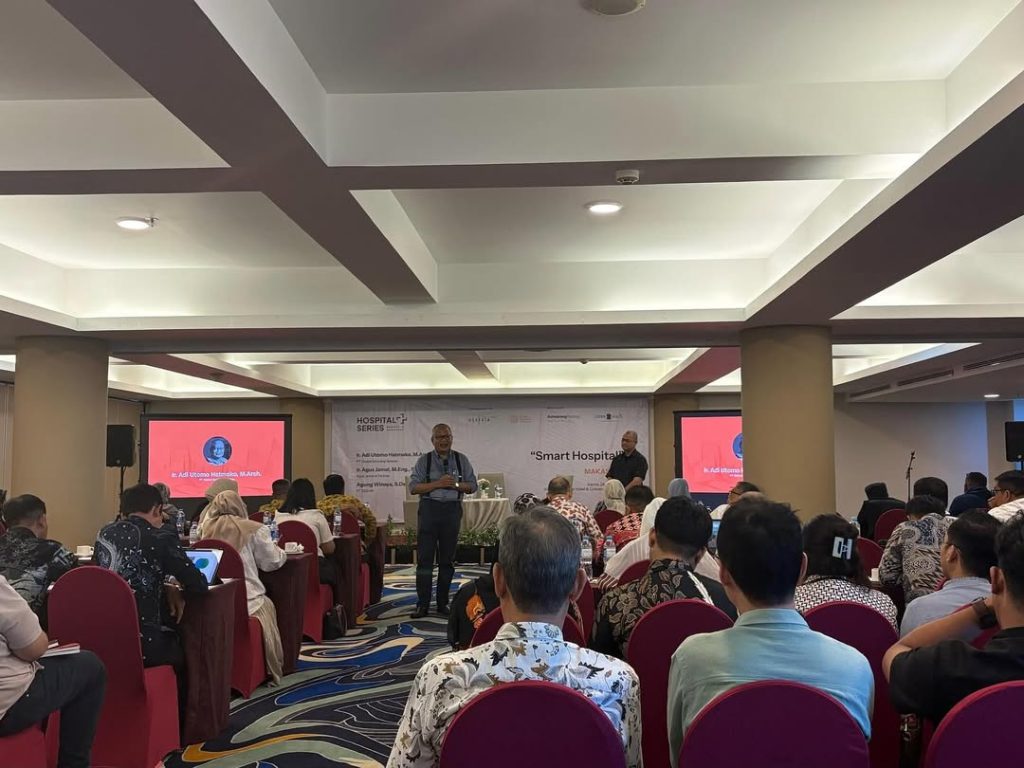
The participation of Ir. Adi Utomo Hatmoko, M.Arch., a lecturer at the Department of Architecture at Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM) and a practicing architect, as a speaker at the Hospital Series on April 24, 2025, reflects the vital role of academics in bridging knowledge and real-world practice. Held at the Kapoposang Meeting Room, Aston Makassar Hotel & Convention Center from 09:00 to 15:00 WITA, the event saw Pak Adi—his common nickname—share his insights on the growing trend of smart hospitals.
This regular event, organized by P.T. Global Rancang Selaras in cities across Indonesia, is especially relevant given the rapid advancement of technology and the increasing demands of modern healthcare systems. In this forum, Pak Adi covered key aspects of hospital design, including design concept development, feasibility studies, hospital zoning, and the basic types of spaces in hospital layouts. He also elaborated on what makes a hospital “smart,” starting from its definition to its practical implications. Some of the smart hospital concepts he presented included: patient-centered care, operational efficiency, advanced diagnostic tools, enhanced communication, AI and data-driven decision making, smart infrastructure and sustainability, robotic assistance, cybersecurity and data protection, smart supply chain management, and patient empowerment and engagement. He emphasized that hospital architecture should support or even help drive the transformation toward these concepts. During the session, Pak Adi shared more than eight case studies from his past and ongoing projects to give participants a clearer understanding of smart hospital implementation.
Importantly, Pak Adi also highlighted the critical role of sustainable architecture in modern hospital design. Through the smart hospital approach, designs must respond to environmental challenges, such as using renewable energy, safe medical waste management, and optimizing natural ventilation and daylight. This aligns with SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure and SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities. Another essential point is the emphasis on efficiency and user comfort, which ultimately contributes to SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being by improving patient health outcomes and overall well-being.
This forum served not only as a knowledge-sharing platform but also as a space for interdisciplinary collaboration among architects, healthcare professionals, property developers, and other stakeholders. Events like this help broaden public awareness—especially among those in the architecture and healthcare sectors—of the importance of smart and sustainable design approaches. This initiative reinforces the commitment of Universitas Gadjah Mada and its academic community to support the global agenda through innovation in architecture and healthcare.
Reported by Rindi Dwi Cahyati