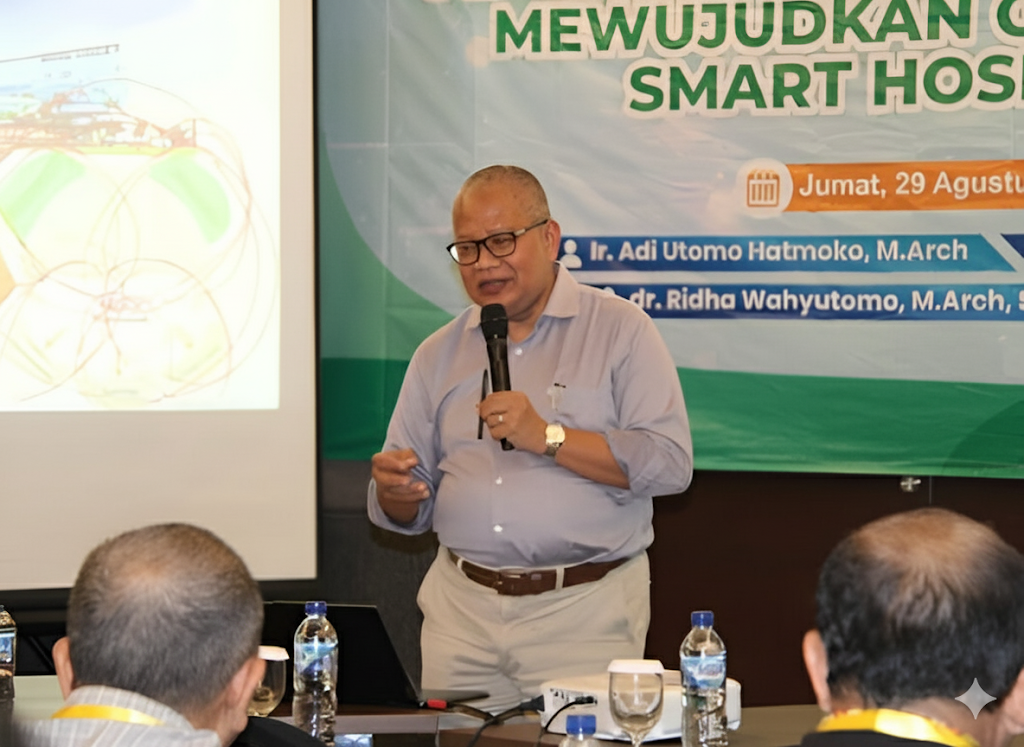
“A hospital is no longer just a place to seek treatment, but a living space that is intelligent and environmentally friendly.” This statement became the central theme of a workshop organized by the Indonesian Hospital Association (PERSI) Central Java Region. The event took place on Friday, August 29, 2025, at the Grand Mercure Hotel, Solo Baru. The workshop carried the theme Transformation of Indonesian Hospital Business in the Era of Change, a topic highly relevant to today’s healthcare facility challenges.
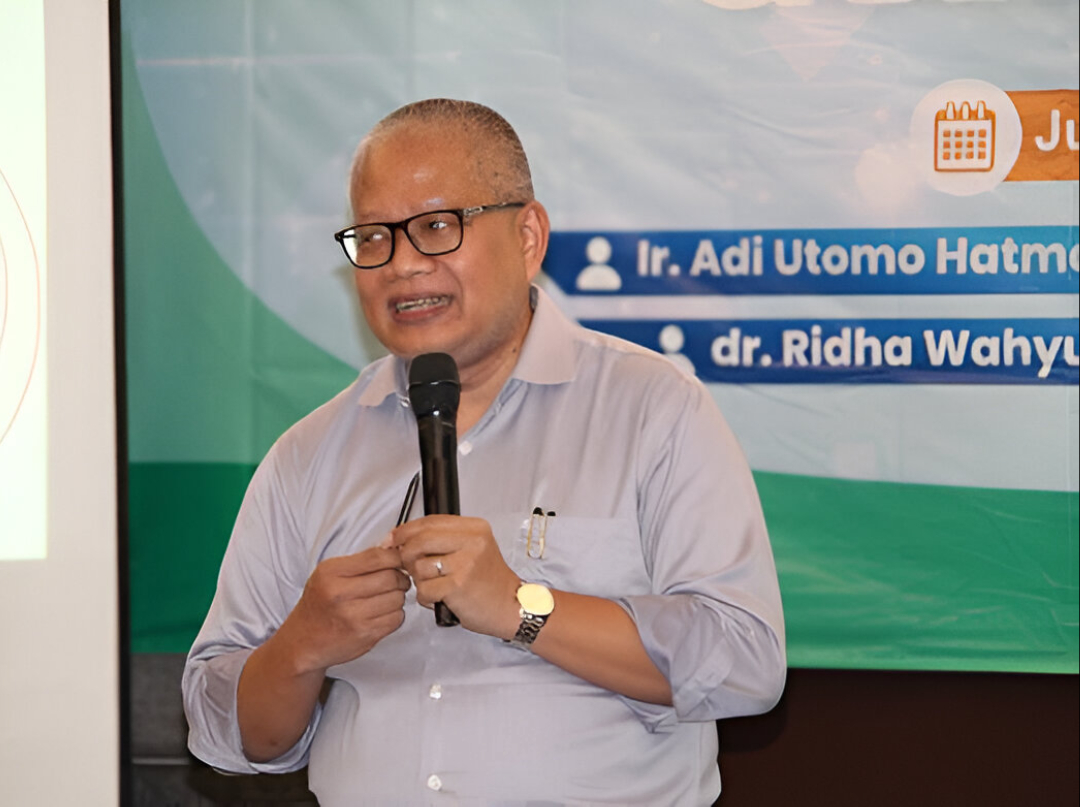
Ir. Ar. Adi Utomo Hatmoko, M.Arch., IAI., AA., attended as the keynote speaker of the event. He delivered a presentation on Smart & Green Hospital, illustrating how hospitals can adapt to the demands of a changing era. The topic drew attention because it combines safety, technology, and sustainability into a unified design approach.
In his presentation, Mr. Adi outlined the fundamentals of comprehensive hospital planning. He explained strategic design process diagrams, hospital concepts, feasibility studies, masterplans, and spatial zoning in a structured way. He emphasized that every space within a hospital has its own specific function that cannot be separated from aspects of patient safety and comfort.
The term SMART in Smart Hospital refers to five essential pillars: Safe, Quality, Secure, Friendly, and Affordable. These principles are integrated with green design to create hospitals that are more efficient and patient-centered. This includes patient-centered care, advanced diagnostic equipment, AI-driven decision-making, strong communication systems, and sustainable smart infrastructure.
Beyond theory, Mr. Adi also presented several case studies of hospitals designed by his team. These case studies helped participants understand the practical implementation of the smart & green hospital concept. With concrete examples, participants could better visualize how design principles can be applied in real-world practice.
He also discussed the regulatory frameworks that form the basis of environmentally friendly hospital design. Among these are the Green Hospital Guidelines (Ministry of Health, 2018), the Jakarta Governor Regulation No. 38 of 2012 on Green Buildings, and the Ministry of Public Works and Housing Regulation No. 02 of 2015 on Green Buildings. These regulations provide an important foundation to ensure hospital design aligns with government standards.
The session concluded with an engaging discussion on green architecture. Topics included hospital design strategies, integration with climate and site conditions, energy efficiency, and better water management. The discussion also highlighted international case studies such as the Mayo Clinic, offering inspiration for hospital development in Indonesia.
Through his insights and work, Mr. Adi affirmed that the smart & green hospital concept aligns with SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being, SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities, and SDG 13: Climate Action. By integrating technology, energy efficiency, and environmentally friendly principles into hospital design, he contributes significantly to equitable and sustainable health development. Mr. Adi demonstrated that smart & green hospitals are not merely a trend, but a concrete strategy to address global health challenges. Hospitals, therefore, can become spaces that not only heal, but also safeguard the future.
Reported by Rindi Dwi Cahyati